
One of the reasons for the beauty and interest of Japanese Medaka is the wide variety of species. Differences in colours, eye and fin shapes, patterns give each Medaka a sense of individuality. Those points make each Medaka shine and beautiful.
Japanese Medaka are improved wild Medaka (mainly Minami Medaka). Many “variation patterns” have been created during the improvement process and these patterns are divided into seven groups of 45 species in the “official guidelines of the Japanese Medaka association’s manual of breed classification” published by the Japanese Medaka association.
If you want to know and learn different patterns of Medaka, try remembering these 45 species! Once you can identify these properly then you are an intermediate learner. If you wish to become and expert then try learning “the trait supplement of 40 types and 11 common supplements”. If you can identify all these patterns, that means you are an expert of Medaka.
Contents(Click or tap to move to the relevant content)
・Characteristics of wild Medaka
・Variation of Japanese Medaka
・Body color
・Transparent scales
・Eye changes
・iridophore
・Patterns
・Fin changes
・Body shape
・Common supplement


Japanese Medaka originated from wild Medaka.Therefore, it is important to understand the characteristics of wild Medaka before learning about Japanese Medaka. (Names ofdiagram above apply to both wild and Japanese Medaka)
<Features of wild Medaka>
| body color | Brown |
| eyes | They are neither small nor large in relation to their body size and don’t protrude. Eyes are black. |
| gill lids | The part attached to the gills that covers through when fish breathes. Those of Japanese Medaka are not transparent. |
| whole body | They are not glittery or shiny on the back. |
| fins | The size and shape of the body is in proportion to the body size as shown in the diagram above.They aren’t too large, too small or too long in relation to body size. Dorsal, caudal, anal and ventral fins are all composed of soft striate and fin membranes. |
| body shape | Shaped as shown in the diagram above. |

As mentioned above, there are 45 different patterns in seven groups of Japanese Medaka which have been altered for various parts of the body. In addition, there are also 40 trait supplements which further subdivide the characteristics with respect to 16 of the 45 species.
In addition to those, there are 11 different traits called “common supplements”. These include trait supplements that are subdivided across more than one of the 45 different trait types or conversely traits that are difficult to determine which type they are subdivided from.
Trait supplements and common supplements could be incorporated into traits if they start to appear in Medaka on a stable basis and if they gain recognition in Japan.
In all, there are 96 species of improved Japanese Medaka. New traits are discovered every year so they will continue to fascinate us with new variation patterns.
<List of traits>


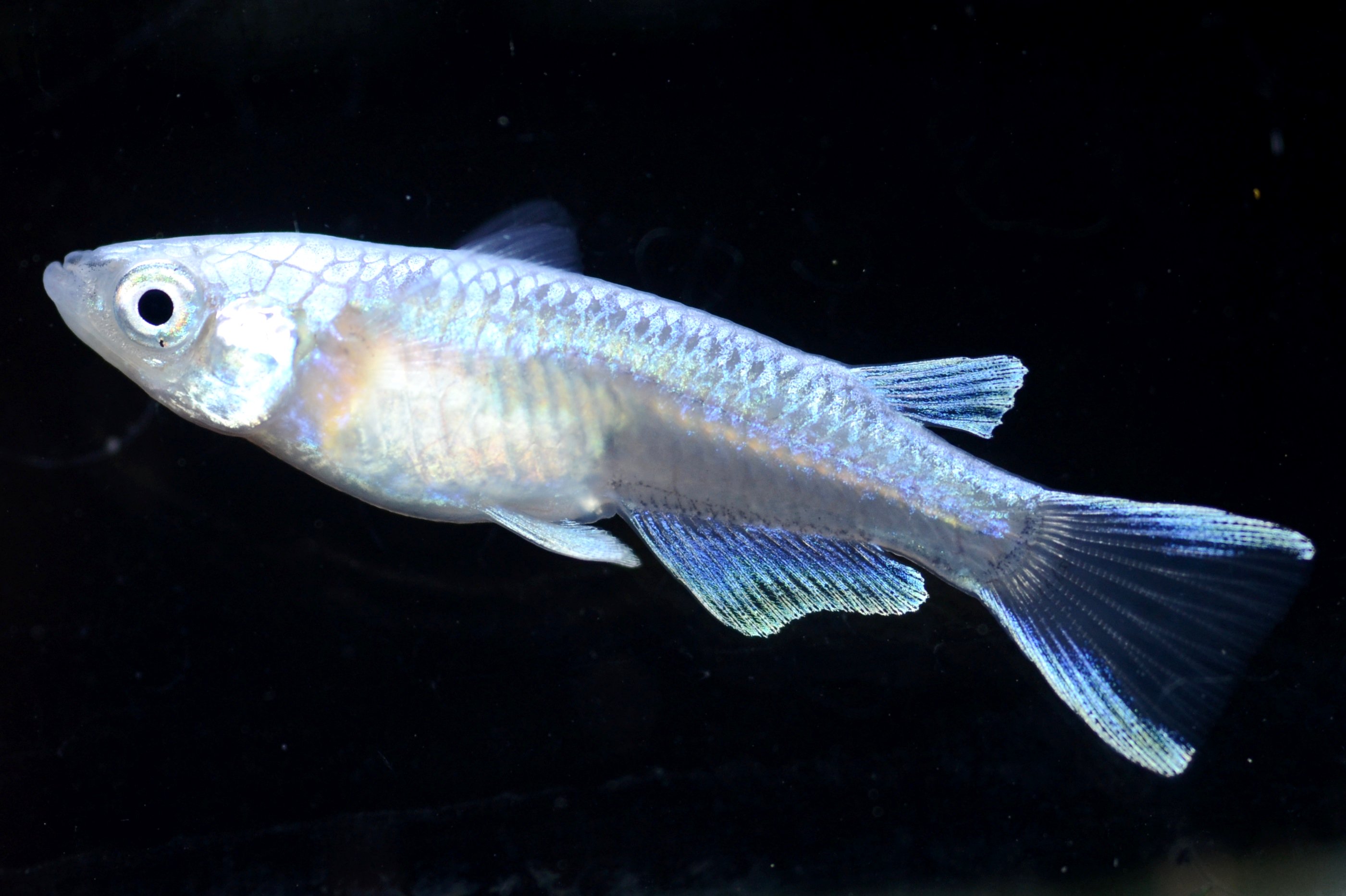
The body color of wild Medaka is”brown”.Japanese Medaka have 10 different colors (including brown).


A “Trait supplement” for body color exists for the following three types.
Click here
・White
(ⅰ)Cream |
It is a cream color with more yellow than white. Also called silky body color. |
・Blue
(ⅱ)Pale blue |
It has a pale blue color. This color is usually referred to as blue body color. |
(ⅲ)Purple blue
 |
It has a blackish blue color. |
(ⅳ)Green
 |
It has a greenish blue color. |
(ⅴ)Fin yellow
 |
The body color is blue, but the fins and head are yellow. It is also called "Silver Medaka". |
・Black
(ⅰ)Fin yellow-scaled.jpg) |
The body is brownish-black with yellow, and each fin also has yellow. |


The same ones as wild Medaka are called "normal scales" and there are two other patterns which the grill cover part is transparent.

There are two types of trait supplements which relate to transparent scales.
Click here
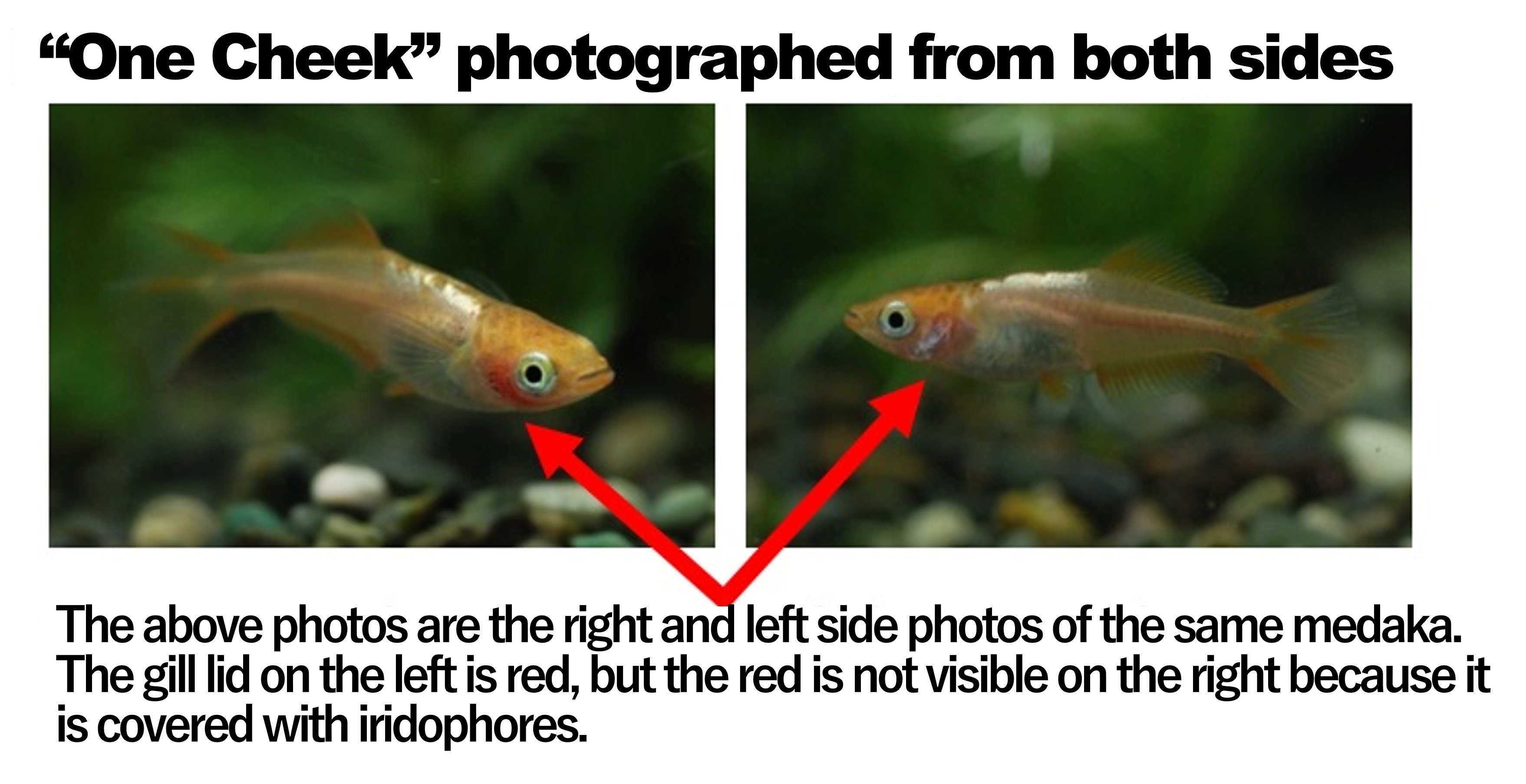
(ⅰ)One cheek
The red transparent scales are only visible on either the left or right side.
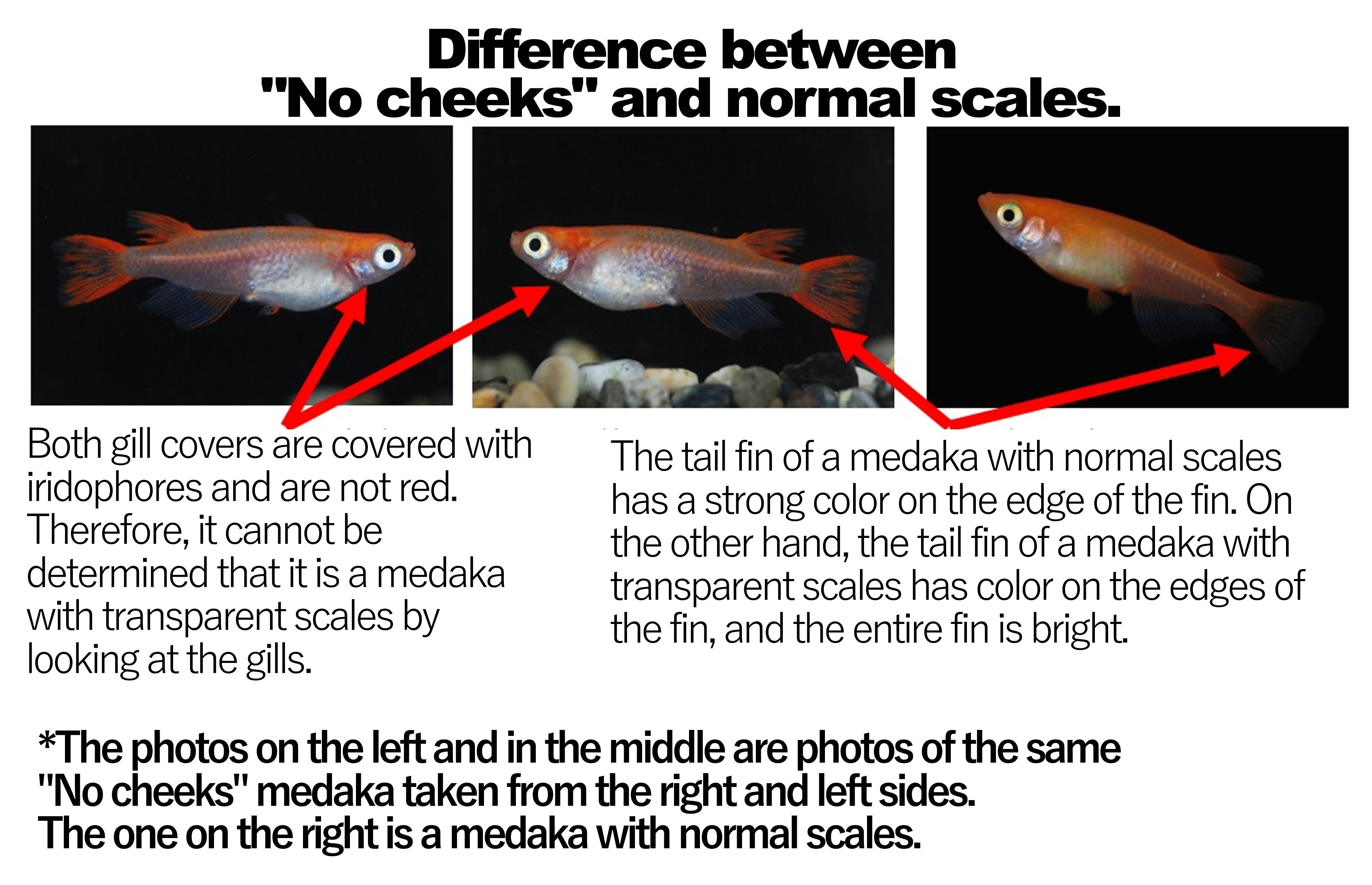
(ⅱ)No cheeks
Although the gill lids are not red, they do have characteristics such as "the body color becomes slightly transparent", "color appears in the fins", and "partial body color disappears.''
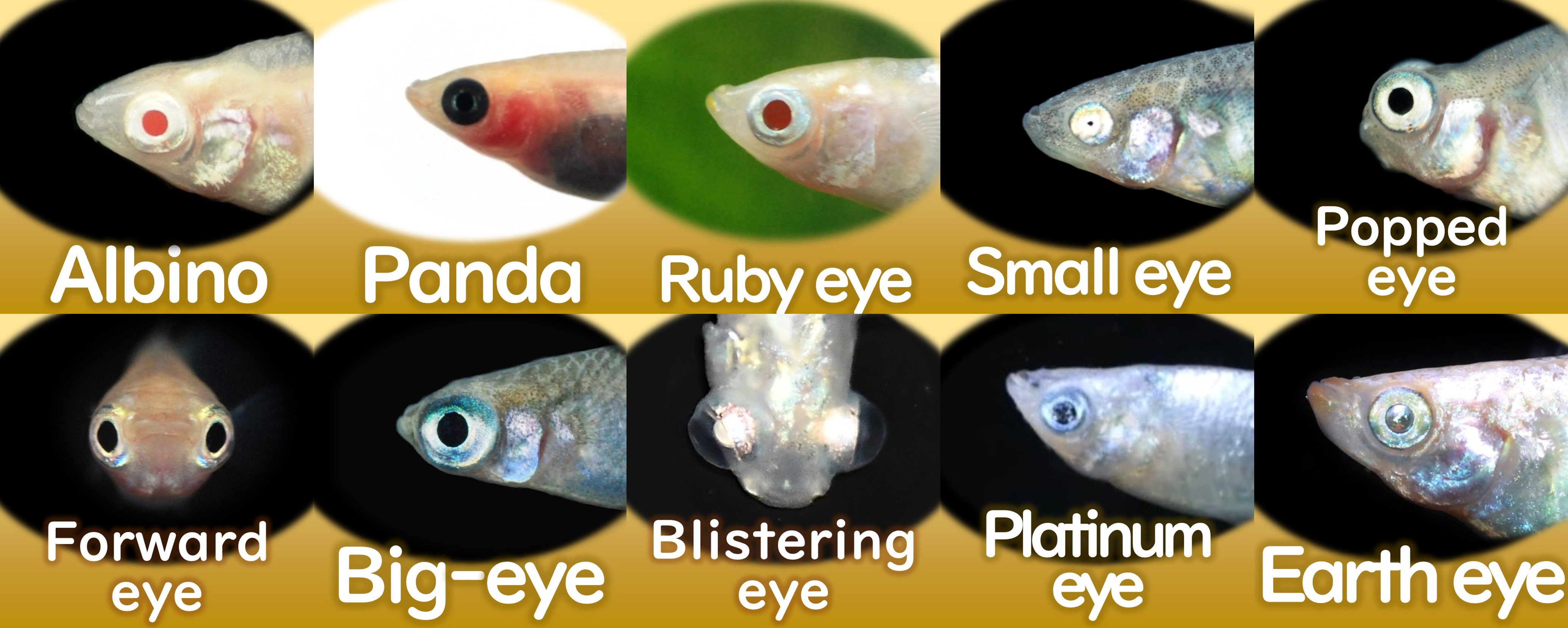



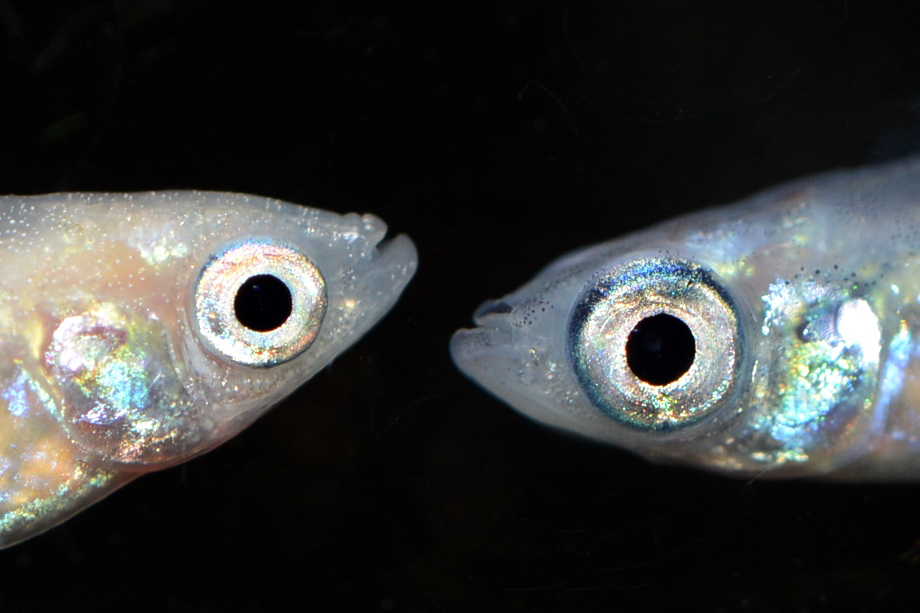
There are 10 variations in the shapes and colours of wild Medaka eyes.


Click here
(ⅰ)Change colorThe color of the eyes changes from red to black depending on the viewing angle.
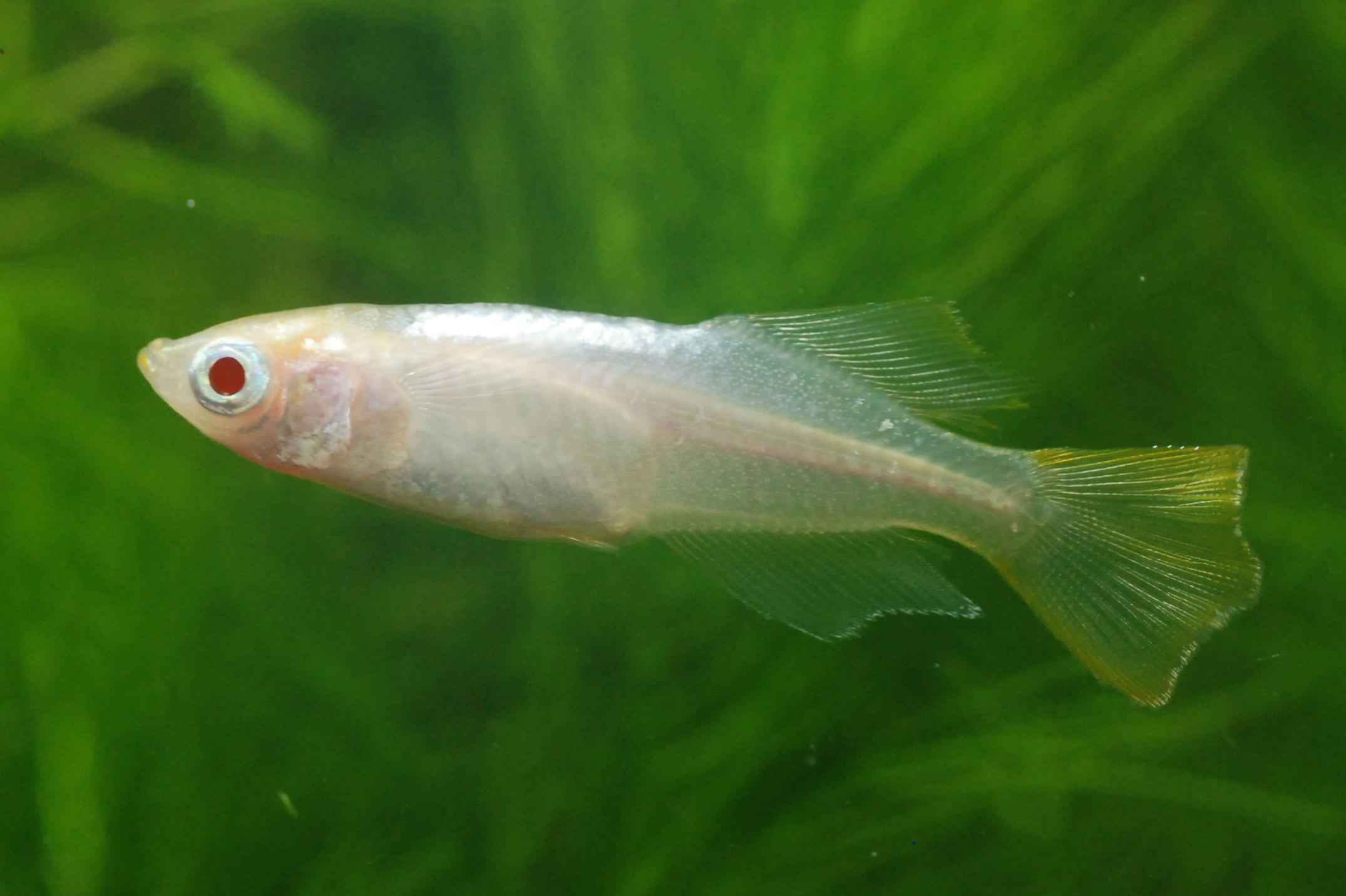




Click here
(ⅰ)Change colorThe eye color changes from deep red to black depending on the viewing angle.
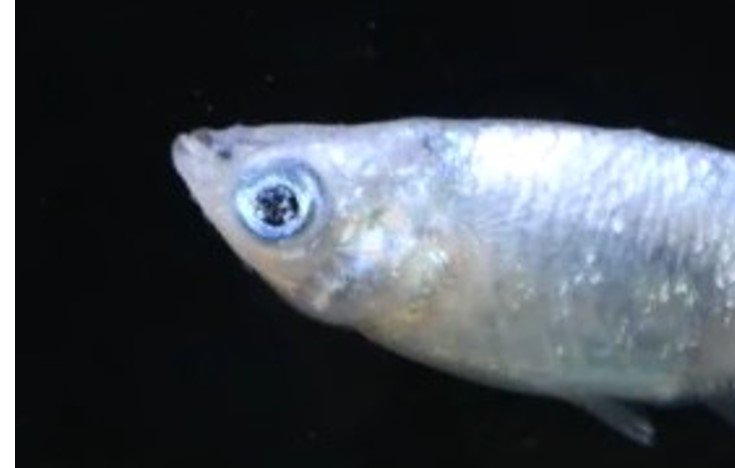
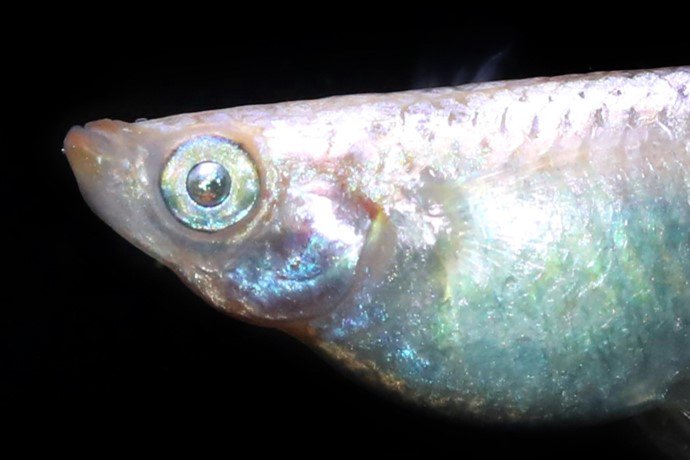



Click here
(ⅰ)Blue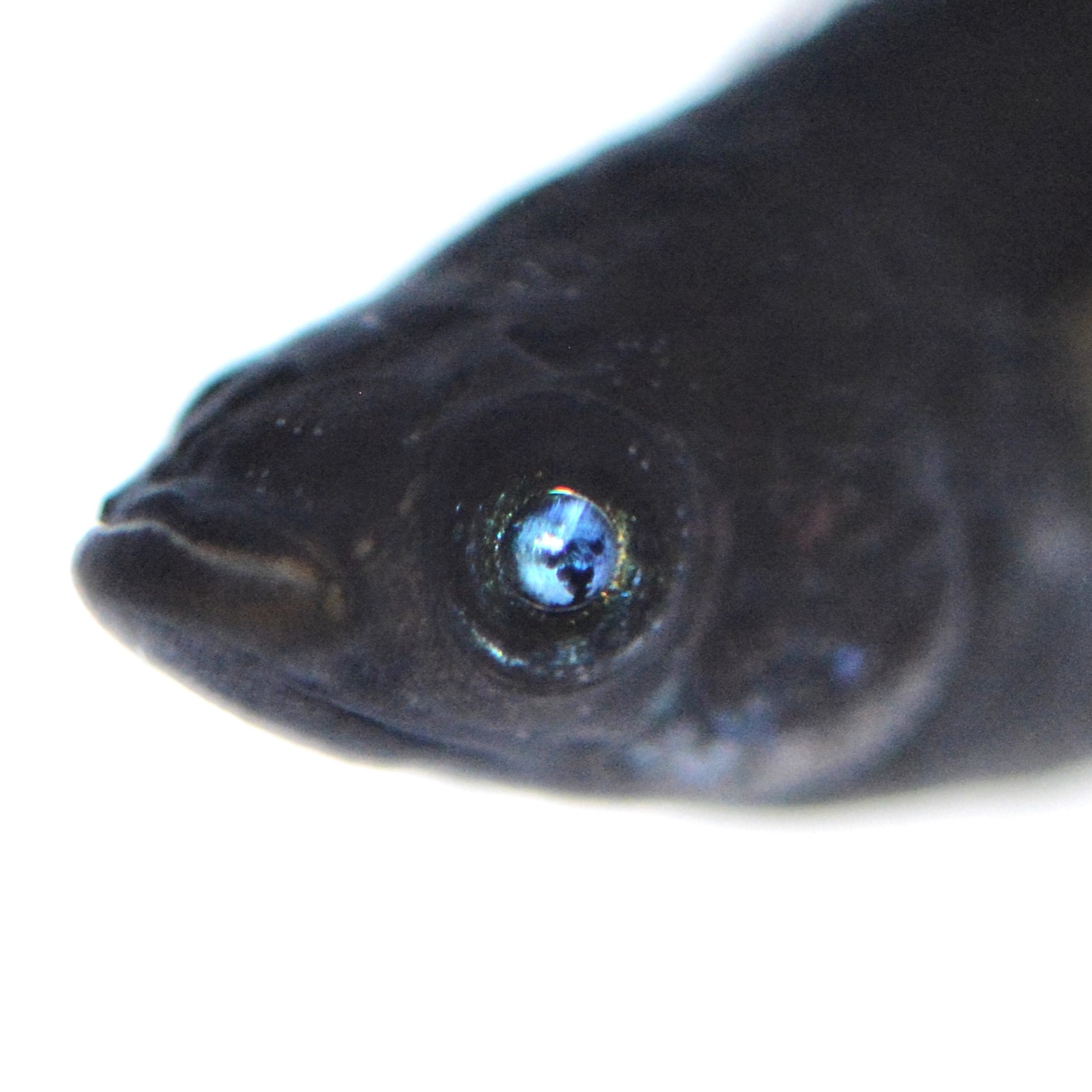 |
The pupils of the eyes are blue. |
(ⅱ)Silver
 |
The pupils of the eyes are silver. |
*background adaptation
The Medaka’s body becomes darker when placed in a black aquarium and whiter when placed in a white aquarium.This change in body colour is called background adaptation.


.jpg)
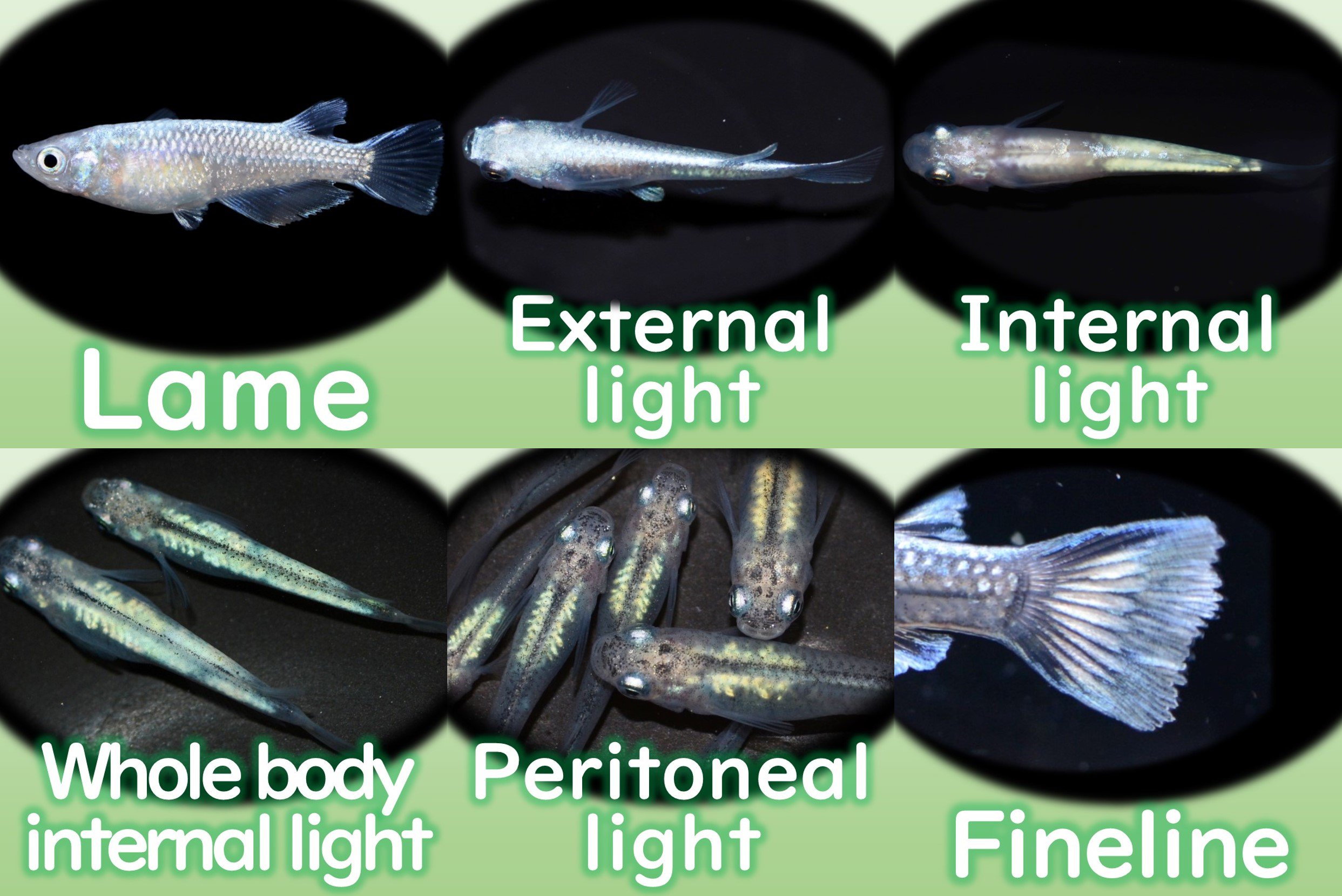




There are six different patterns of lame or sparkle on the whole body, back, inside the body and on the fins.


Click here
(ⅰ)White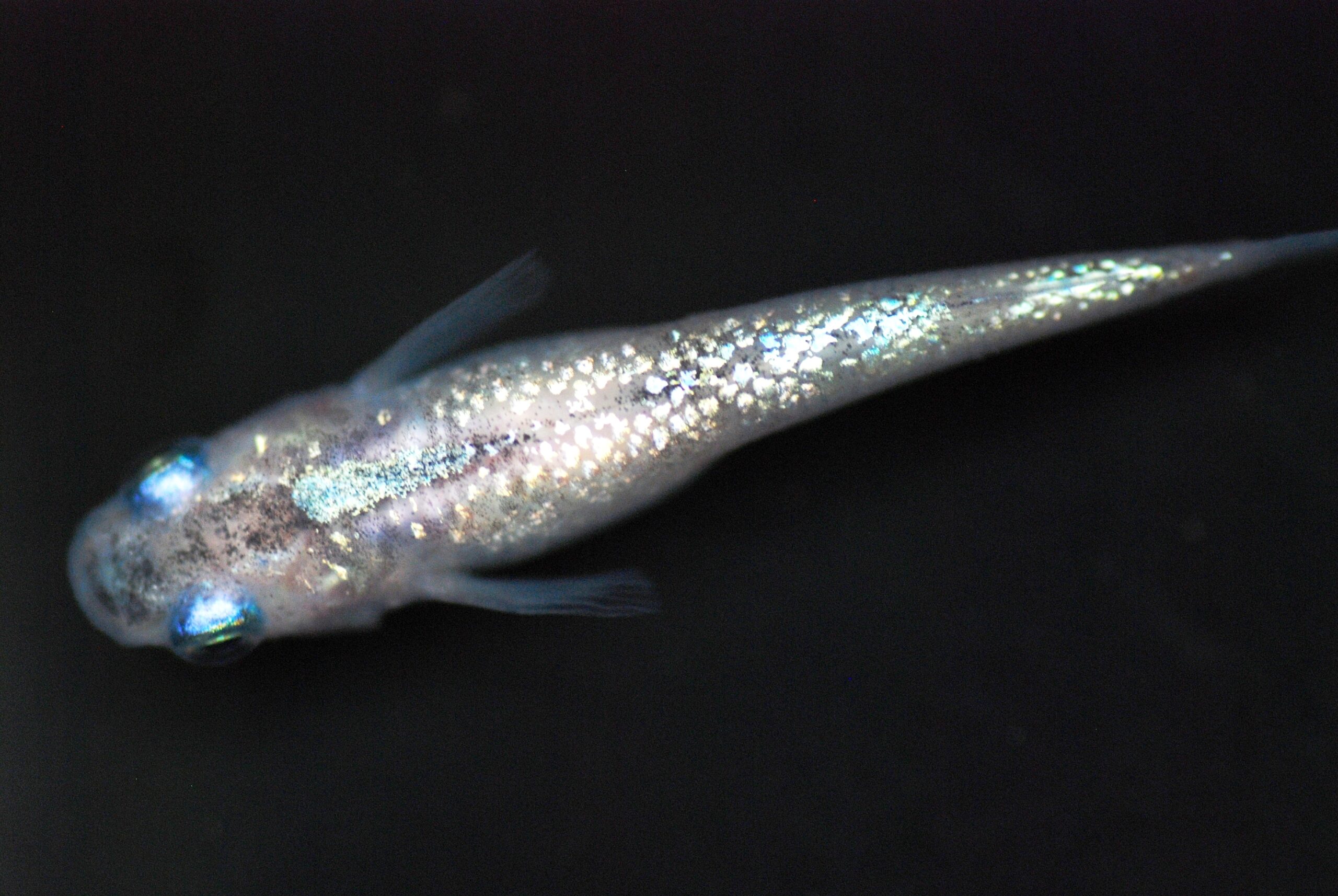 |
The glitter color appears as a single white color. |
(ⅱ)Blue
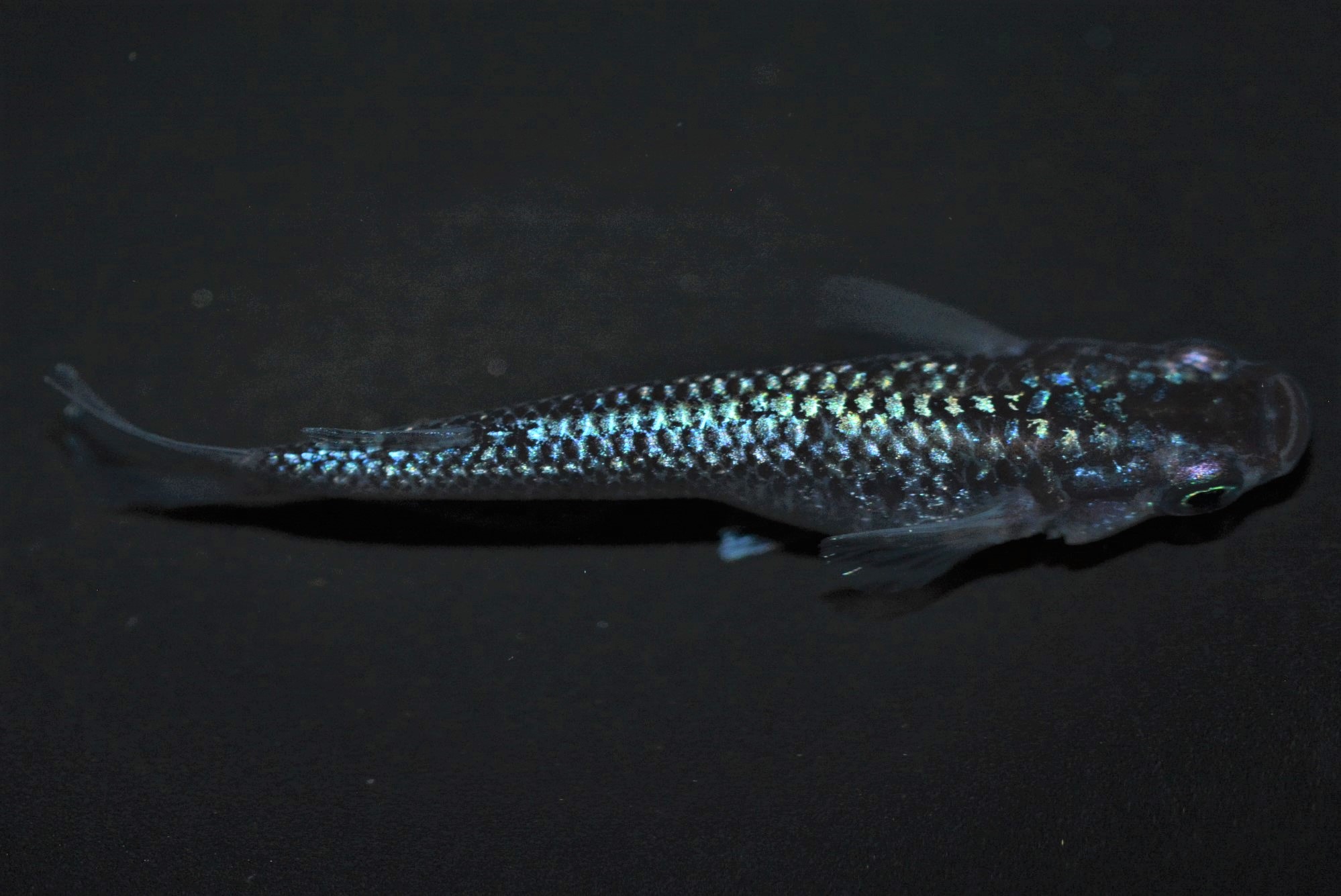 |
The glitter color is expressed as a single blue color. |
(ⅲ)Multicolor
.jpg) |
Various colors of glitter appear at the same time, including blue, orange, gold, and pink. |


Click here
(ⅰ)White.jpg) |
The color of the external light is white. The thicker the layer of light, the whiter it tends to be. |
(ⅱ)Blue
.jpg) |
The color of the external light is bluish-white. This color is generally referred to as external light. |
(ⅲ)Gold
.jpg) |
The color of the external light is golden. |
(ⅳ)Green
.jpg) |
The color of the external light is green. Also called green light. |
(ⅴ)Two colors
.jpg) |
A pattern in which the color of the external light glow differs between the head and back. |
(ⅵ)Head light
.jpg) |
A pattern in which the color of external light shines only on the head. |
(ⅶ)Side light
-scaled.jpg) |
A pattern in which the color of external light appears on the side of the body. The shape of the light varies, such as a band-like glow or a linear glow along the bones. |
(ⅷ)Scale light
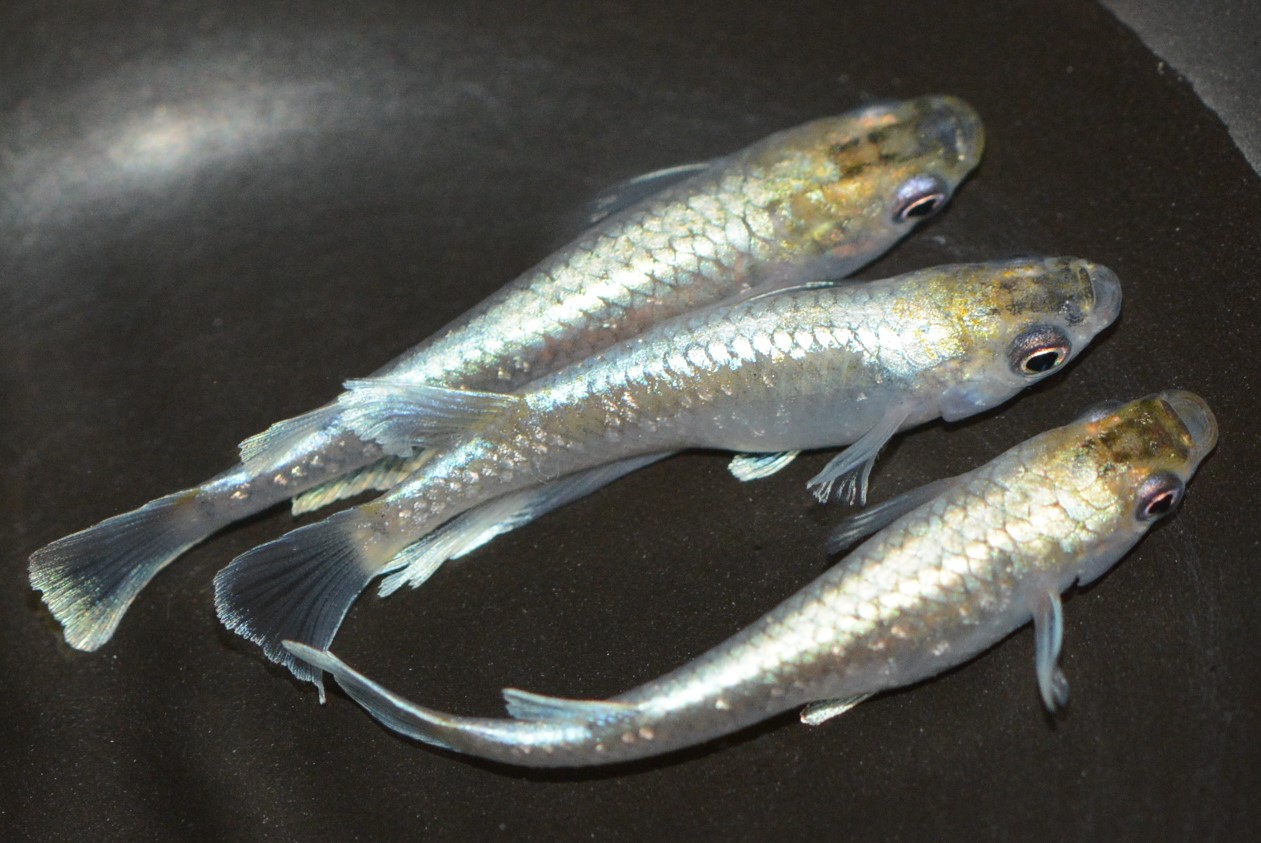 |
A pattern in which the glow of external light appears in a mesh pattern along the scales. |
(ⅸ)Spot lame
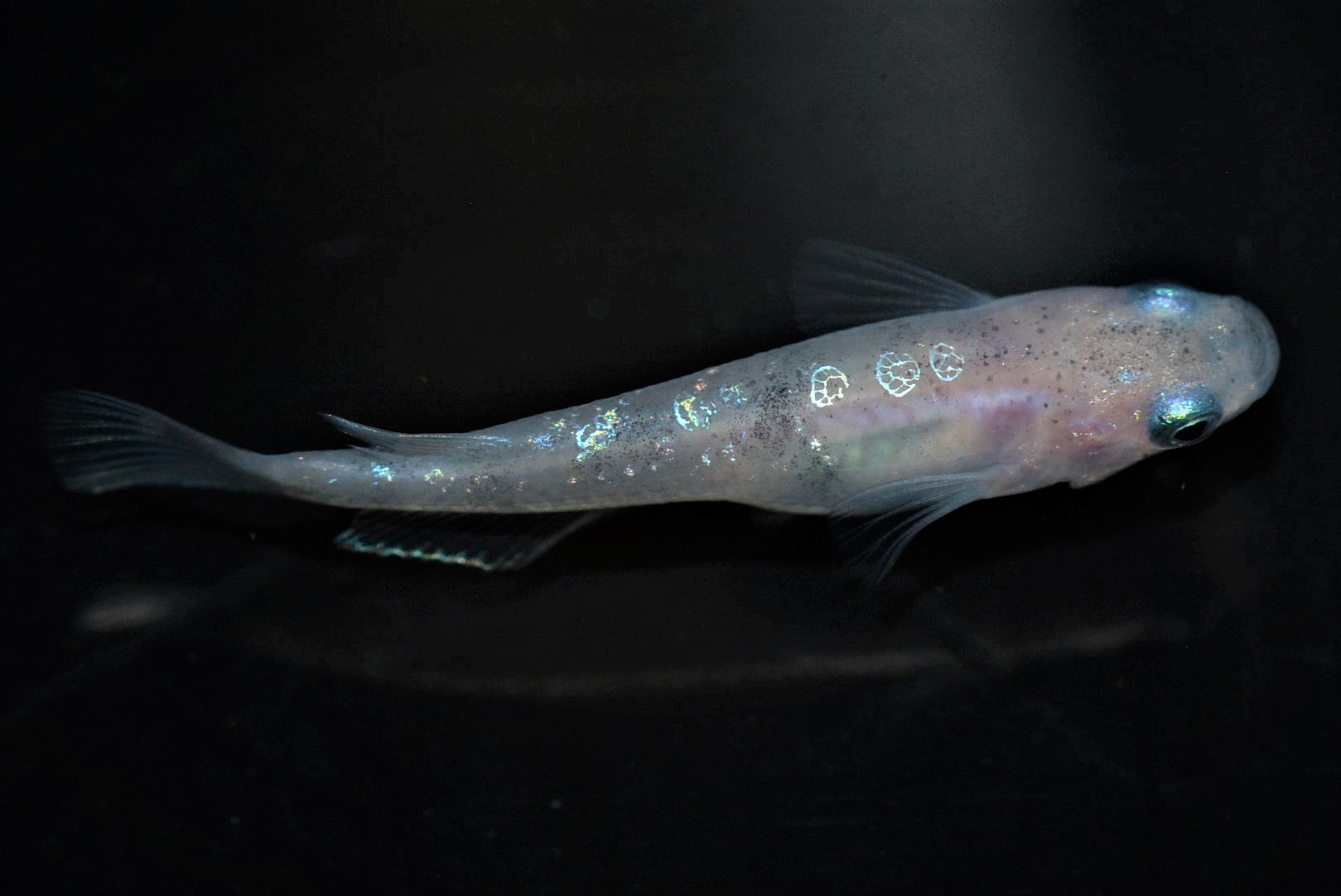 |
A pattern in which the brilliance of external light appears intermittently. |


Click here
(ⅰ)Blue white-scaled.jpg) |
The color of the internal light is bluish-white. This color is generally referred to as internal light. |
(ⅱ)Green
.jpg) |
The color of the internal light is green. |
(ⅲ)Orange
-scaled.jpg) |
The color of the internal light is orange. |
(ⅳ)Blue
.jpg) |
The color of the internal light is blue. |
(ⅴ)Multicolor
-2.jpg) |
The color of the glow of the internal light is two or more colors. |
(ⅵ)Oral light
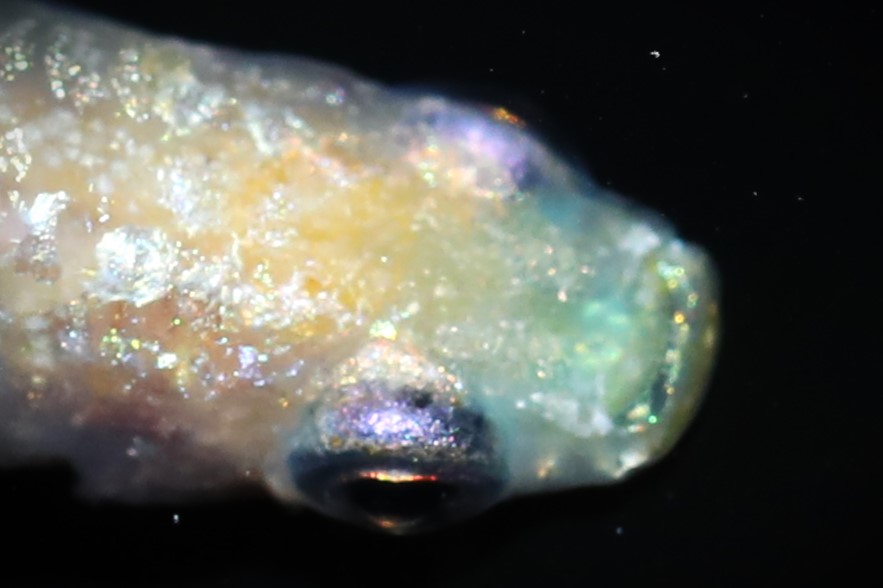 |
The glow of internal light appears in the mouth. |


Click here
(ⅰ)Multicolor.jpg) |
It is a whole-body internal light in which the light is multicolored. Most of the light inside the body is multicolored. The color of light varies, such as blue, green, and orange. |


Click here
(ⅰ)Blue.jpg) |
This is a peritoneal light where the color of the light is blue. |
(ⅱ)Orange
.jpg) |
It is a peritoneal light where the color of the light becomes orange. |
(ⅲ)Multicolor
.jpg) |
It is a peritoneal light in which the light has two or more colors. |
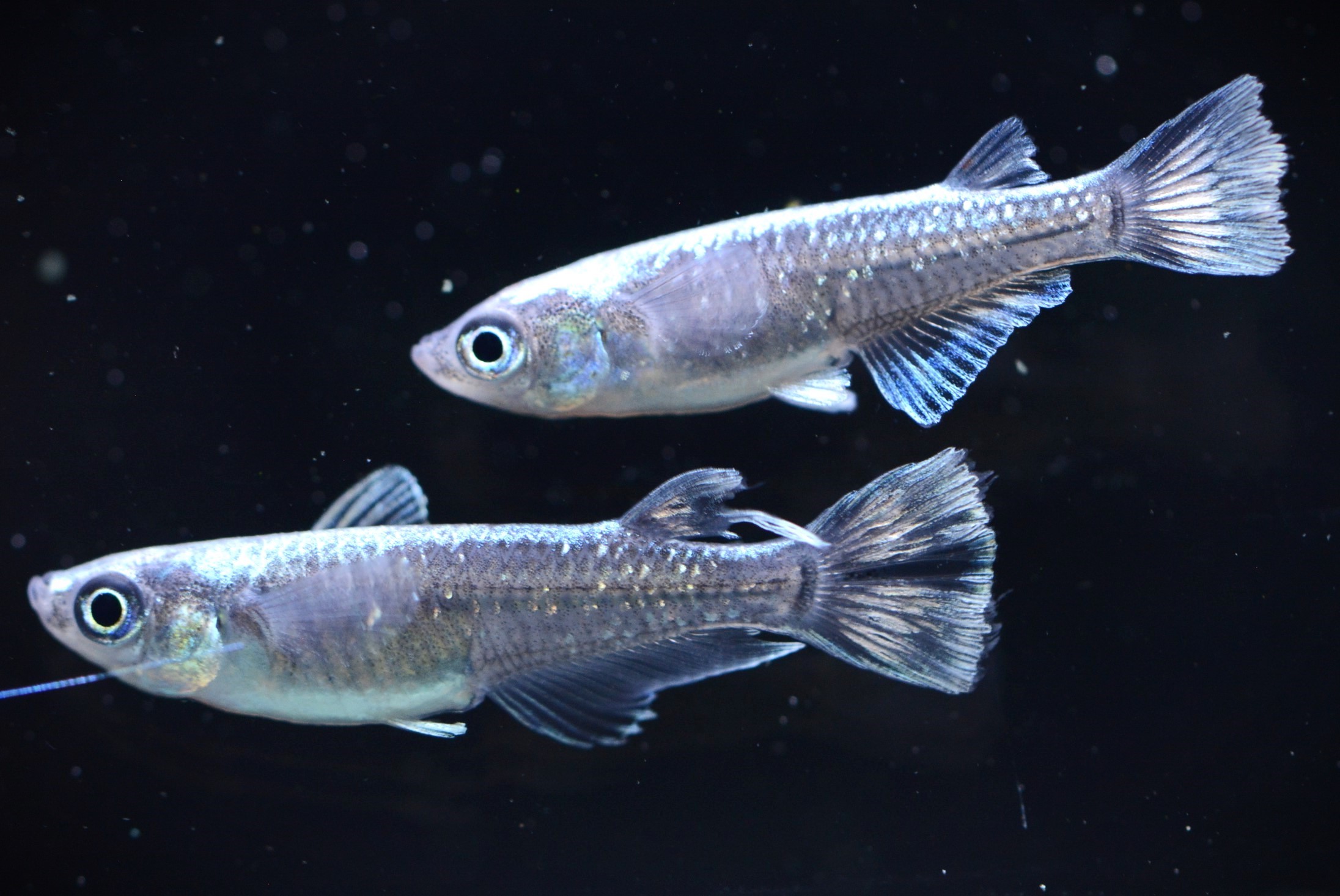



There are two different patterns of patterns on the body.
.jpg)

Click here
(ⅰ)No background adaptation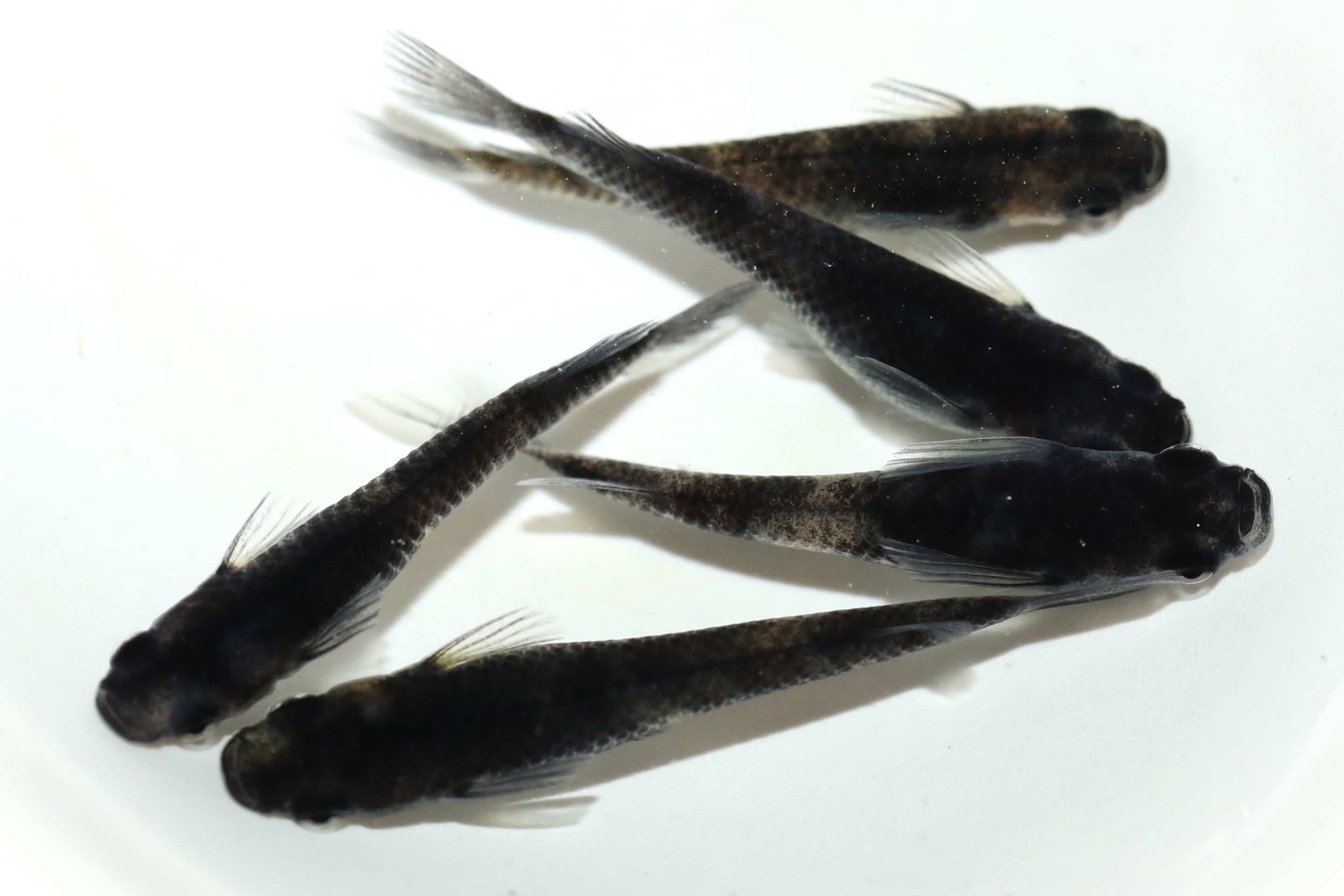 |
The spots do not fade even in a bright environment such as a white container. |

Black tends to develop on the edges of the scales on the head and tends to cluster in the centre of the scales closer to the caudal fin.



There are 12 different patterns with varying length and shapes of fins.
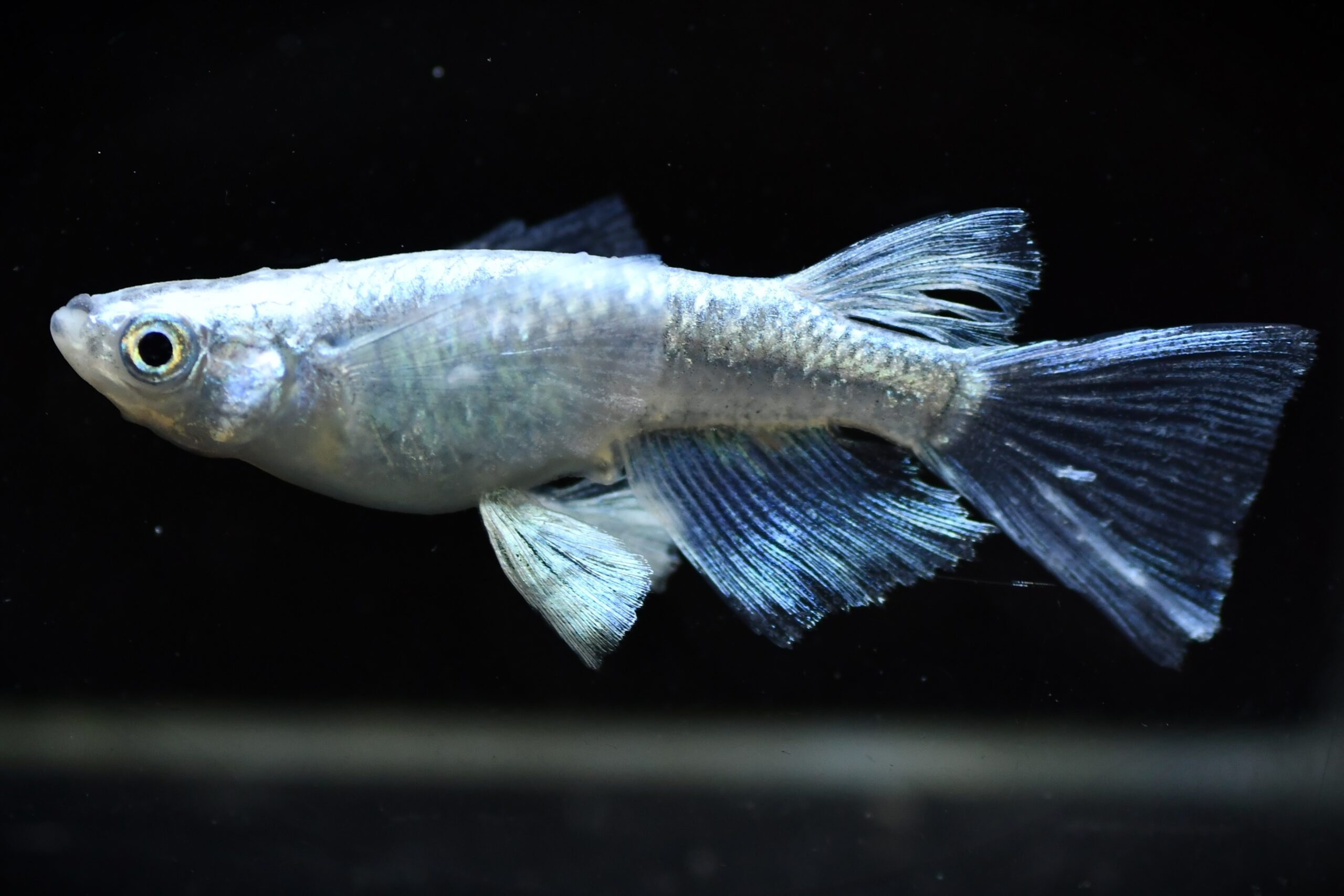
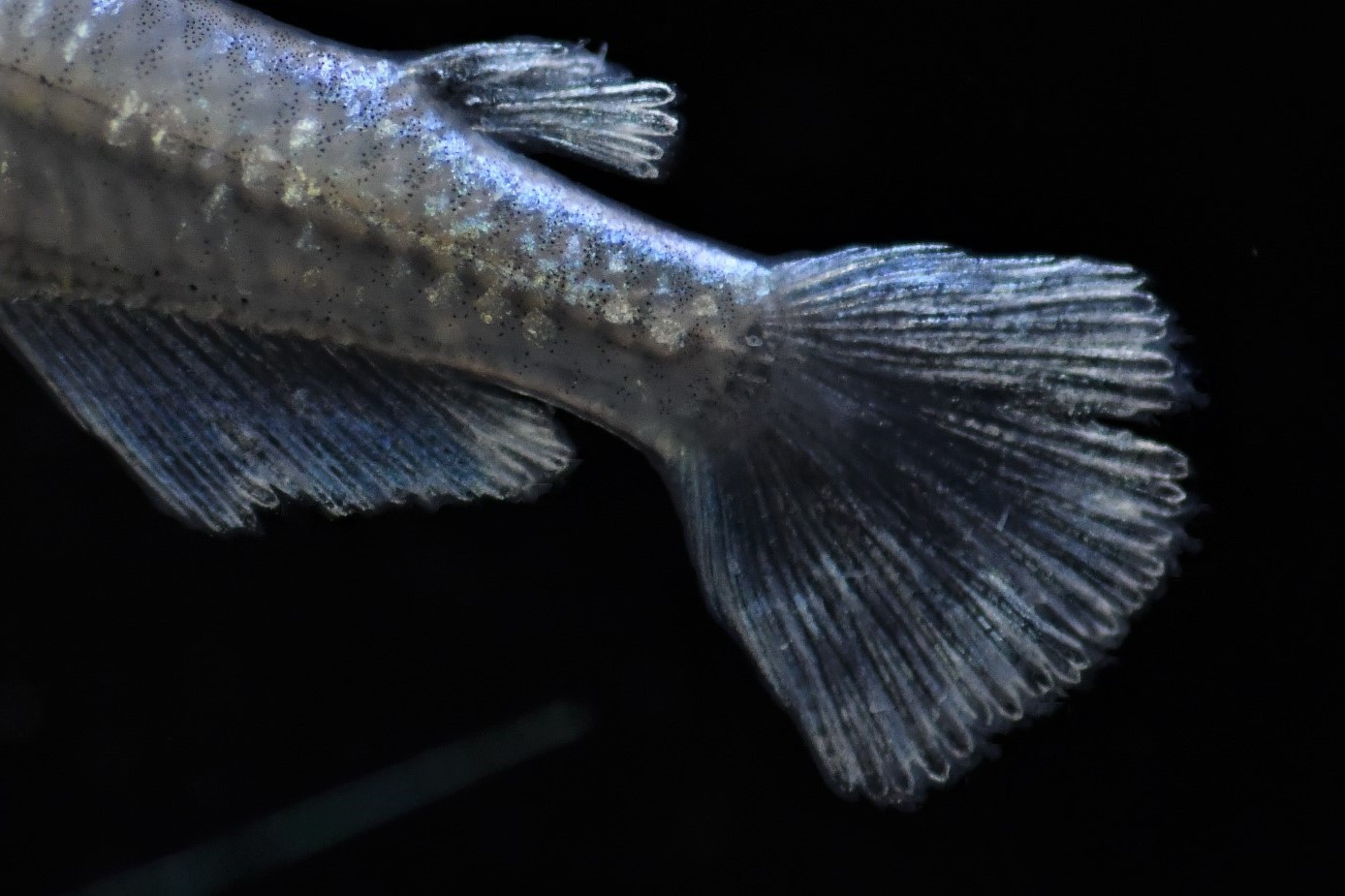
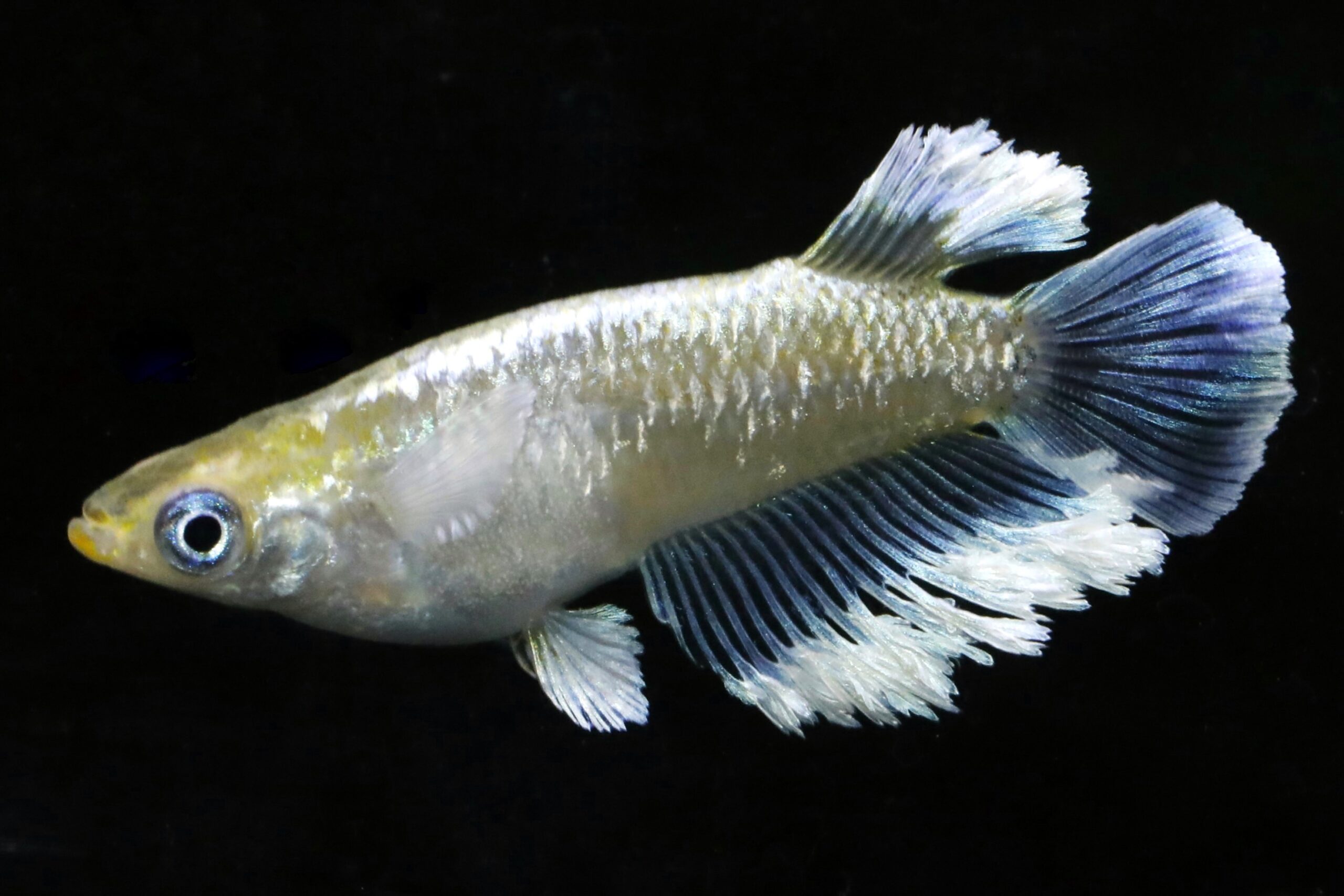
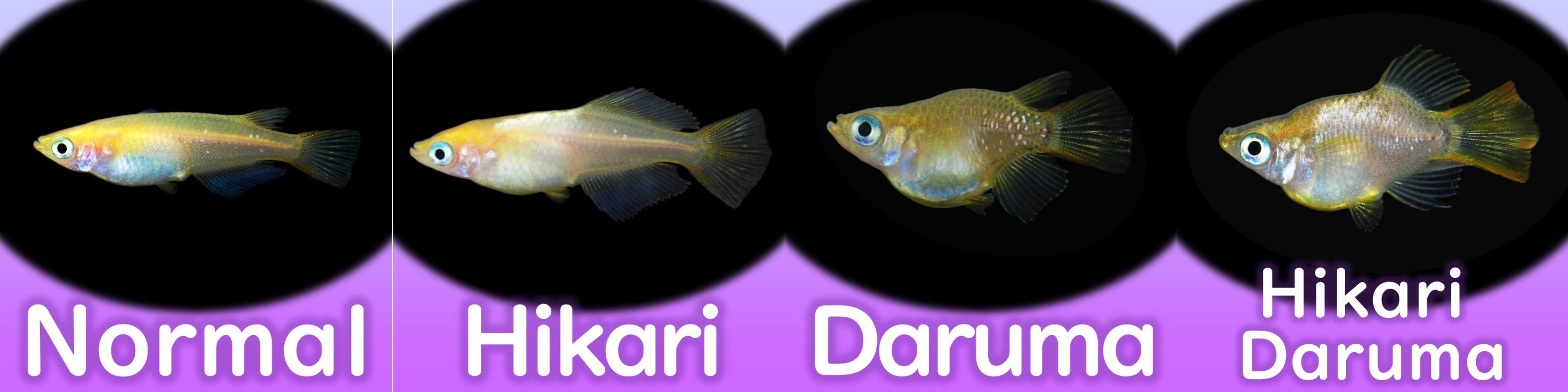














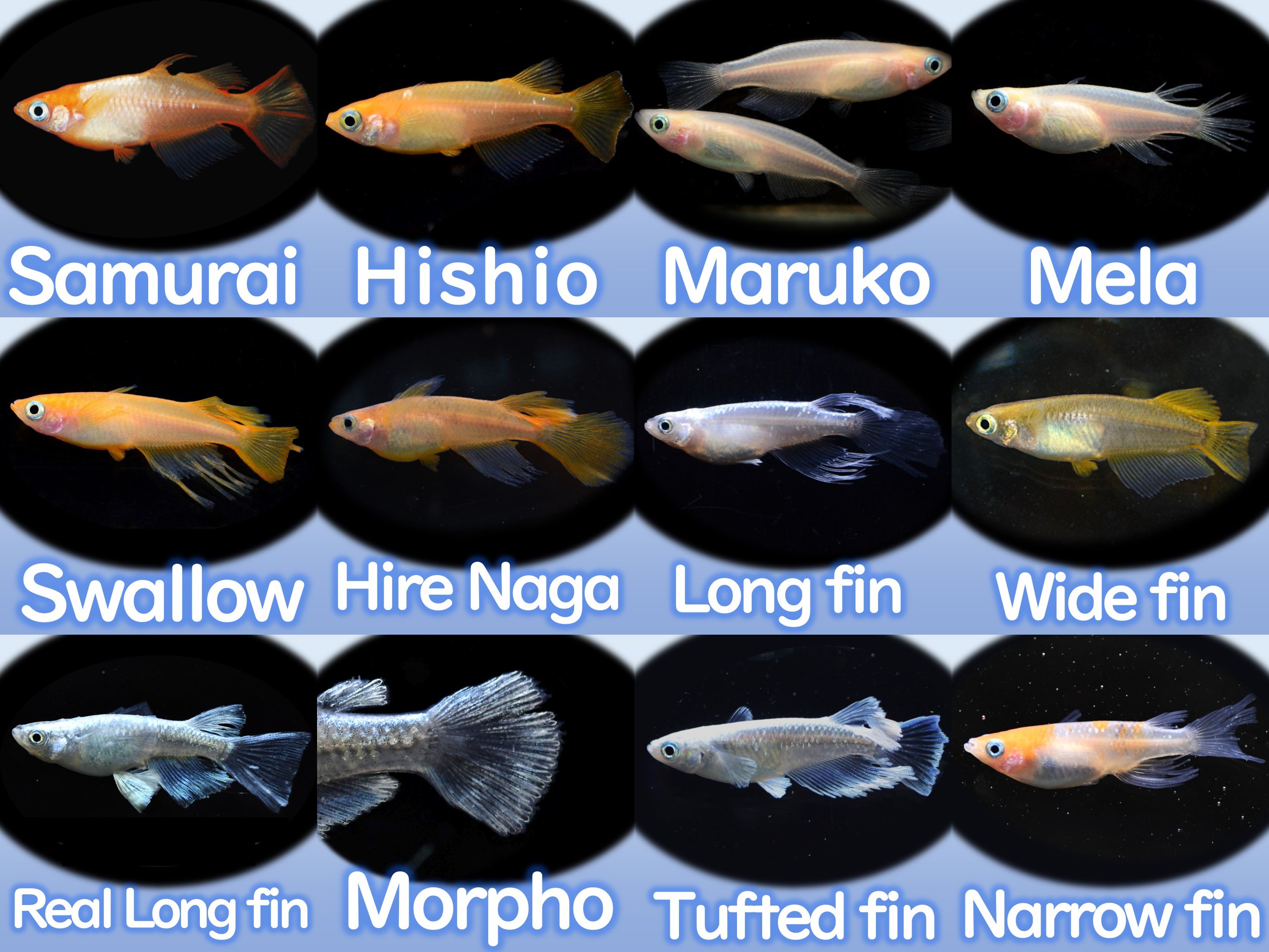
The shape of wild medaka is the "normal" form, and there are three other types.


Click here
(ⅰ)Strong light.jpg) |
A strong light is an individual with a Hikari form whose back light is stronger than normal (different from "external light"). The light appears as a silver streak without interruption. |
(ⅱ)Silver belt
.png) |
In the silver belt, the light on the back of the Hikari form becomes stronger, and the light covers the sides of the body, creating a band-like light. |
The back is swollen due to the shortened body length.
They are not good at swimming and are sensitive to changes in water temperature and quality. This makes breeding and spawning difficult.
The fixation rate is low, and even if two Daruma form are crossed, the normal form, semi-Daruma form, and Daruma form will be produced.
Also called balloon medaka or short body.

What is Daruma? :
Daruma is a doll which is regarded in Japan as a good-luck charm to make wishes come true. It is shaped like a shortened human being.


Click here
(ⅰ)Semi-Daruma form-scaled.jpg) |
The body length is shorter than the normal form and longer than the Daruma form. |


Click here
(ⅰ)Strong light.jpg) |
This is an individual with a Hikari Daruma form, and the light on its back is stronger than normal (different from the "external light"). The light appears as a silver streak without interruption. |
(ⅱ)Silver belt
.jpg) |
The light on Hikari daruma's back becomes stronger, and the light covers the sides of its body, creating a band-shaped light. |


Features which are subdivided across more than one of the 45 of features introduced so far. Also conversely features that are difficult to determine which type they are subdivided form are listed as common supplements.
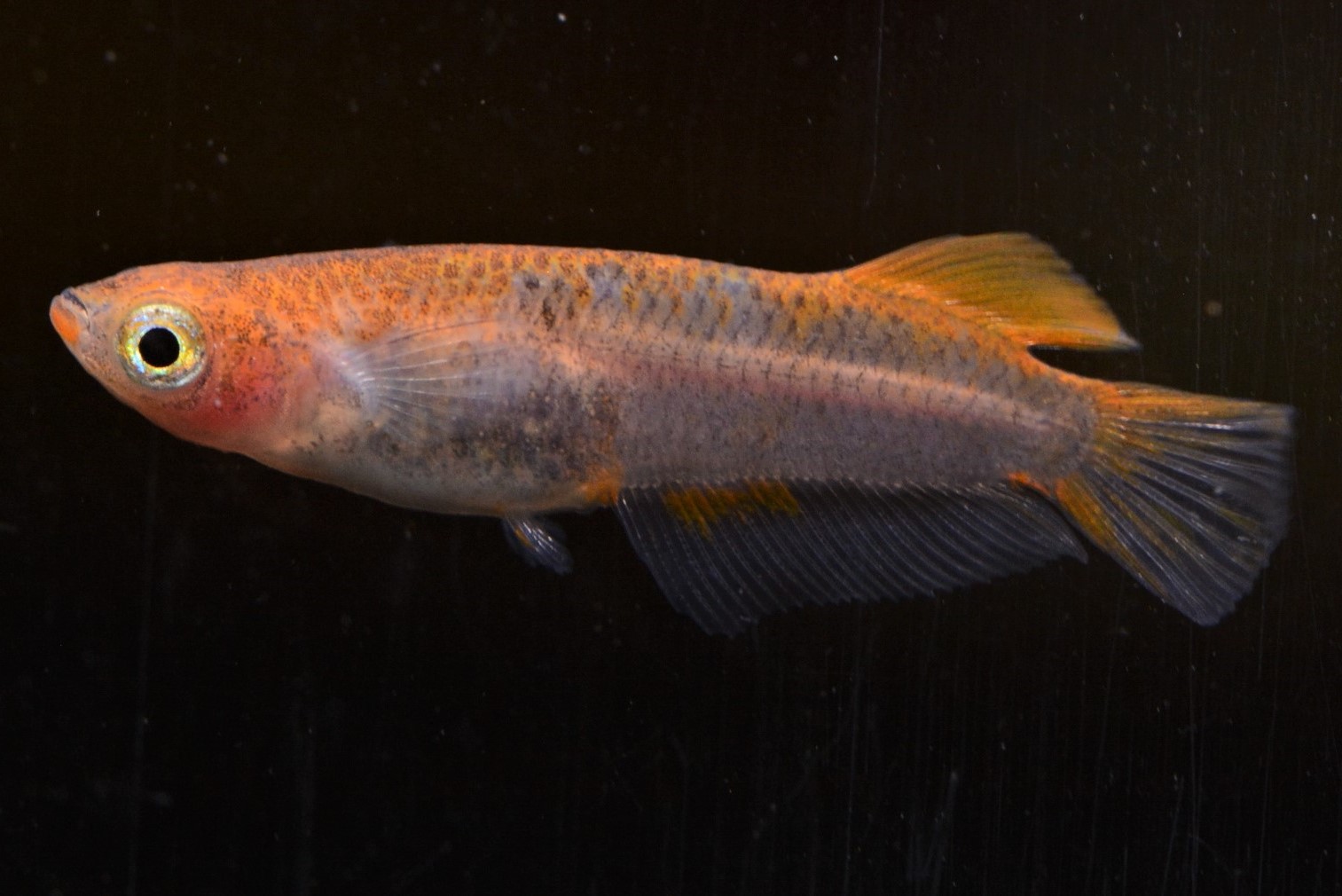
・The fins are more vivid and conspicuous than the body color
・Color develops in positions where it would normally be difficult to see it
Above points are considered to be "Hirebi". Both of these characteristics are difficult to be expressed in normal scales and "Hirebi" is generally found in transparent scaled varieties.
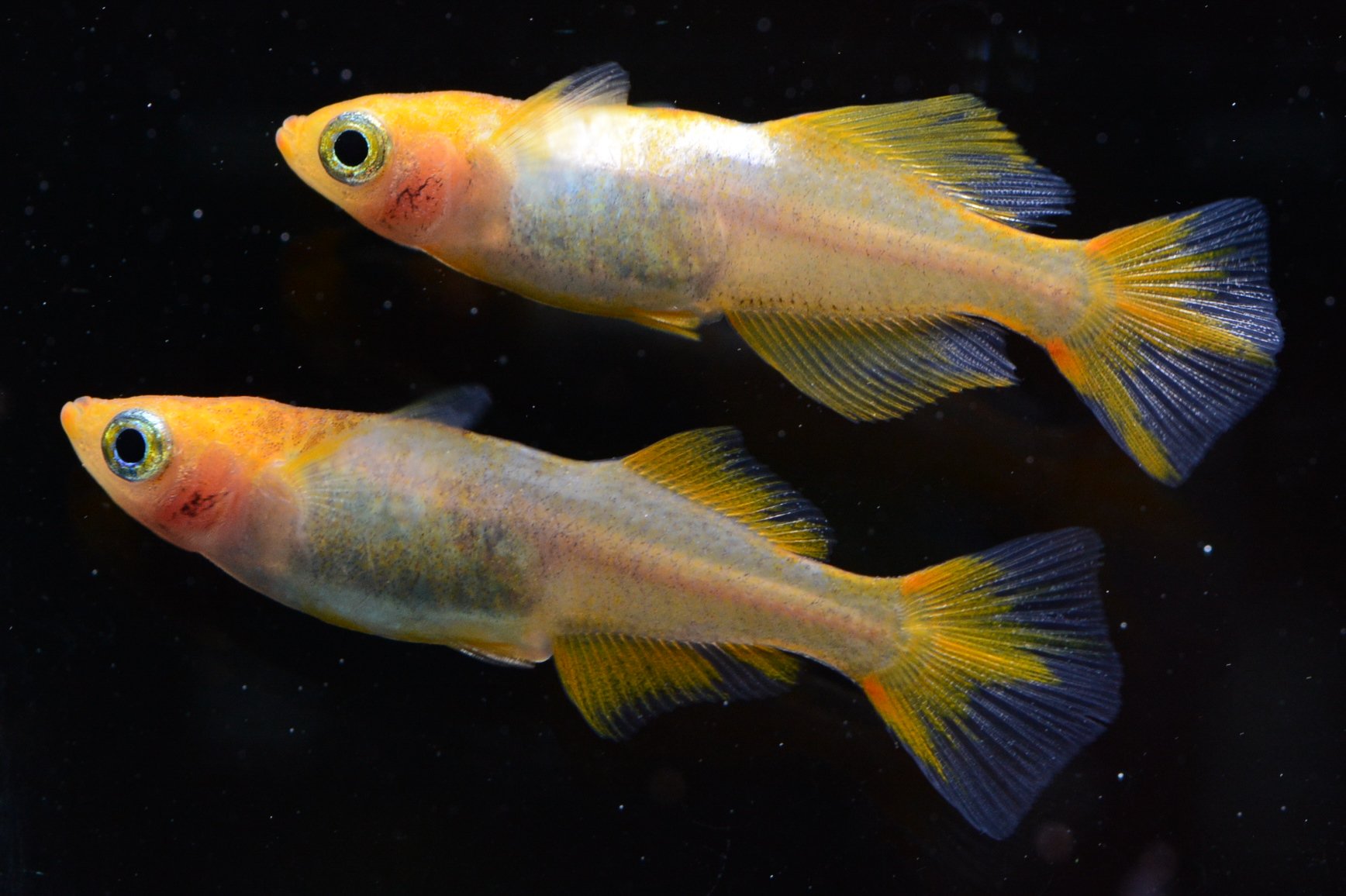



・Normally, "external light" should be viewed from above, but the light from the fins is so strong that it is okay to view it from the side.
・The light intensity doesnt change depending on the angle so the light of the fins are strong.


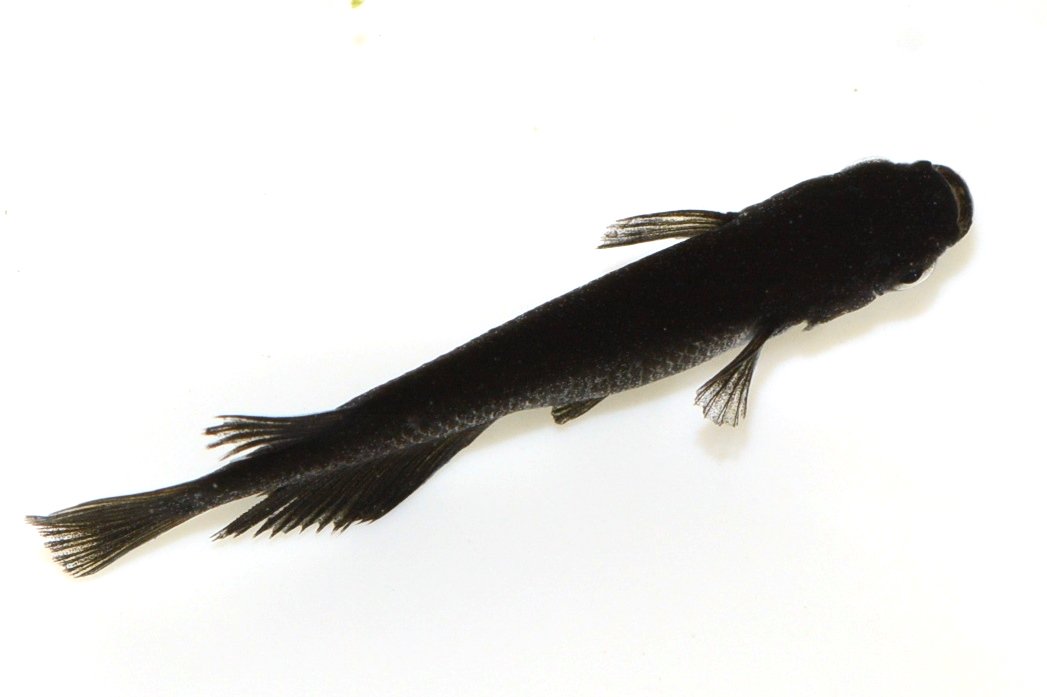
This has the characteristic that its body color doesn’t change in a white water aquarium. Normally in a white water aquarium a black fish turns grey. Also the spots and black rims lose their patterns. However, Medaka with this common supplement have a darker black color even in a white water aquarium.






| 日 | 月 | 火 | 水 | 木 | 金 | 土 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
カテゴリーから探す
- 厳選メダカの現物販売
- 全品3,000円以下!現物販売
- セット販売コーナー
- 全品3,000円以下!セット販売コーナー
-
【毎月更新】ピックアップ品種
- 全ての【毎月更新】ピックアップ品種
- 【2025年4月】フロストイエロー
- 【2025年3月】ピンクサファイアNEO
- 【2024年10月】如水〜銀白〜
- 【2024年9月】ミラージュグロウ
- 【2024年8月】フロスト
- 【2024年3月】モルフォ桔梗
- 【2024年1月】ピュアホワイト透明鱗
- 【2023年11月】ミラージュ
- 【2023年10月】如水
- 【2023年8月】菜花
- 【2023年7月】極ラメ星河
- 【2023年5月】ロゼ
- 【2023年4月】さくら
- 【2023年3月】ピンクサファイア
- 【2023年2月】鱗光
- 【2023年1月】琥珀ブルーラメ
- 【2022年12月】禅半月×青蝶半月
- 【2022年11月】出目目前メダカ
- 【2022年10月】MLFH×BMA
- エサ
- 書籍・その他










